Fundamentals of Soft Computing: A Comprehensive Guide

Soft computing is an emerging field that utilizes computational techniques to solve complex problems that cannot be easily solved using traditional hard computing methods. It encompasses various approaches, including fuzzy logic, neural networks, evolutionary algorithms, and probabilistic reasoning. By mimicking human decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, soft computing algorithms offer flexibility, adaptability, and robustness in handling uncertain, imprecise, and incomplete information.
Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic is a mathematical framework that deals with vagueness and impreciseness. It allows the representation of information in linguistic terms, such as "high," "low," or "medium," rather than using precise numerical values. Fuzzy sets, unlike traditional crisp sets, have boundaries that are not clearly defined, allowing for gradual transitions between membership and non-membership.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6887 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 256 pages |
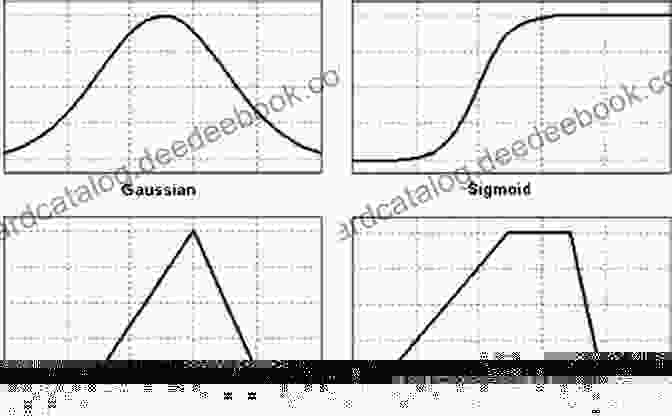
Fuzzy logic systems use fuzzy rules to make decisions. These rules are typically derived from expert knowledge or data and are represented using if-then statements. The input to the system is fuzzified, converting numerical values into fuzzy sets. The fuzzified values are then processed using fuzzy rules to generate a fuzzy output. Finally, the fuzzy output is defuzzified to obtain a crisp numerical value.
Neural Networks
Neural networks are computational models inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. They consist of interconnected nodes, called neurons, that process information in parallel. Neural networks are capable of learning from data, identifying patterns, and making predictions without explicit programming.
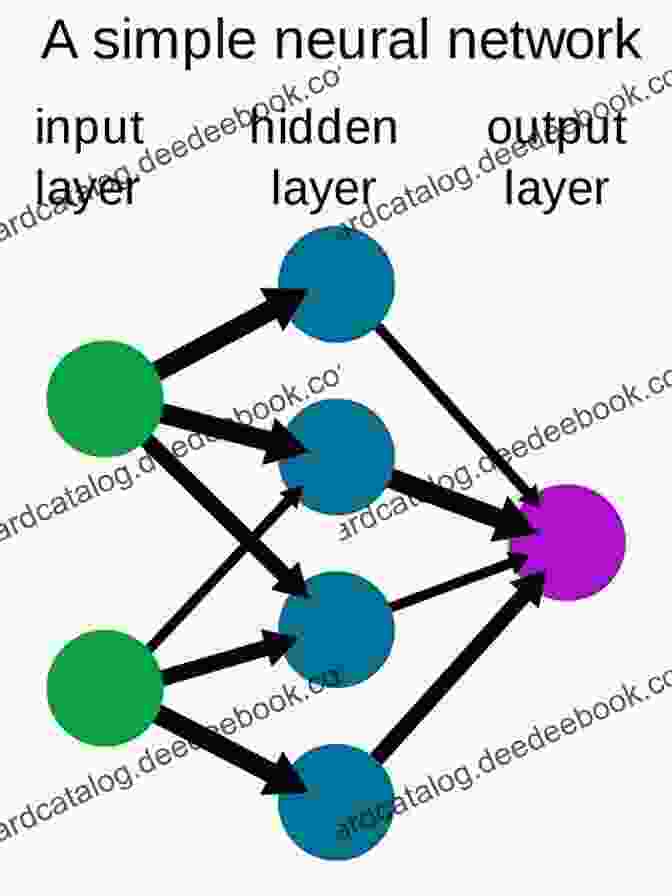
Neural networks are trained using a process called backpropagation. During training, the network is presented with labeled data, and the weights and biases of the neurons are adjusted to minimize the error between the network's predictions and the desired outputs. Trained neural networks can perform various tasks, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
Evolutionary Algorithms
Evolutionary algorithms are optimization techniques inspired by the principles of biological evolution. They simulate the natural selection process to find solutions to complex problems. Evolutionary algorithms start with a population of random solutions and iteratively apply genetic operators, such as crossover and mutation, to evolve better solutions.

Evolutionary algorithms are particularly useful for solving problems where no prior knowledge or explicit rules are available. They can generate diverse solutions and handle problems with multiple optima. Applications of evolutionary algorithms include optimization, scheduling, and design optimization.
Probabilistic Reasoning
Probabilistic reasoning deals with uncertainty and randomness in a quantitative manner. It utilizes probability theory and Bayesian inference to represent and update beliefs based on available evidence. Probabilistic reasoning allows for the fusion of information from multiple sources and the calculation of posterior probabilities, which represent the likelihood of events given the observed data.
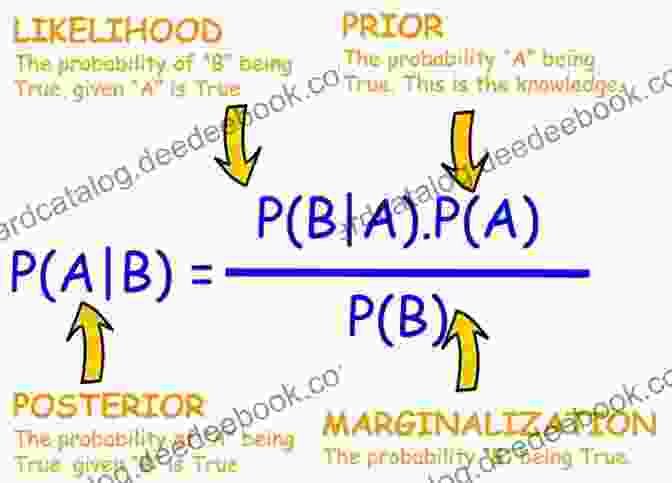
Applications of probabilistic reasoning include risk assessment, decision making under uncertainty, and expert system development. Probabilistic reasoning techniques can handle incomplete and uncertain information, making them suitable for problems where precise data is not available.
Hybrid Soft Computing
Hybrid soft computing combines multiple soft computing approaches to create more robust and effective solutions. By combining the strengths of different techniques, hybrid systems can overcome the limitations of individual methods and tackle complex problems with increased accuracy and efficiency.
For example, a hybrid system may use fuzzy logic to represent imprecise information, neural networks to learn complex patterns, and evolutionary algorithms to optimize the solution. Such a system can leverage the advantages of each technique to provide a comprehensive solution to a wide range of problems.
Applications of Soft Computing
Soft computing has a wide range of applications across various fields, including:
- Control systems
- Data mining
- Expert systems
- Financial forecasting
- Healthcare
- Image processing
- Natural language processing
- Optimization
- Pattern recognition
- Robotics
Advantages of Soft Computing
Soft computing approaches offer several advantages over traditional hard computing methods:
- Flexibility: Soft computing algorithms can handle uncertain, imprecise, and incomplete information, making them suitable for problems where precise data is not available.
- Adaptability: Soft computing systems can learn from data and adapt their behavior accordingly, providing solutions that are tailored to specific problems and environments.
- Robustness: Soft computing algorithms are generally robust and tolerant to noise and errors in input data, making them reliable for real-world applications.
- Transparency: Soft computing methods, such as fuzzy logic and neural networks, are relatively easy to understand and interpret, providing insights into the decision-making process.
Soft computing is a powerful and versatile field that provides effective solutions to complex problems that cannot be easily solved using traditional methods. By utilizing fuzzy logic, neural networks, evolutionary algorithms, and probabilistic reasoning, soft computing techniques offer flexibility, adaptability, robustness, and transparency. Hybrid soft computing systems, which combine multiple soft computing approaches, further enhance the effectiveness and applicability of these techniques. With its wide range of applications and advantages, soft computing is poised to play a significant role in advancing technology and solving real-world challenges in various fields.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6887 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 256 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Novel
Novel Text
Text Story
Story Reader
Reader Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Newspaper
Newspaper Sentence
Sentence Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Library card
Library card Biography
Biography Memoir
Memoir Dictionary
Dictionary Character
Character Catalog
Catalog Borrowing
Borrowing Stacks
Stacks Archives
Archives Research
Research Academic
Academic Reading Room
Reading Room Rare Books
Rare Books Special Collections
Special Collections Interlibrary
Interlibrary Literacy
Literacy Study Group
Study Group Thesis
Thesis Dissertation
Dissertation Storytelling
Storytelling Reading List
Reading List Chris Walter
Chris Walter Nicola Cornick
Nicola Cornick L A Casey
L A Casey Mark Lilla
Mark Lilla Christine Porter
Christine Porter Lennart Thomsen
Lennart Thomsen Chantal Heide
Chantal Heide Scott Jay Marshall Ii
Scott Jay Marshall Ii Marc Leepson
Marc Leepson Rachel Hanna
Rachel Hanna Tony Hillerman
Tony Hillerman Anthony King
Anthony King Pablo Palomino
Pablo Palomino Ai Li
Ai Li Ahmed Sherif
Ahmed Sherif Kent Sasse
Kent Sasse Brandi Davis
Brandi Davis Jemma Wayne
Jemma Wayne Julia Schneiderfeld
Julia Schneiderfeld Tom Rockmore
Tom Rockmore
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Vic ParkerUnderneath the Mango Tree: A Literary and Philosophical Exploration by Ahmet...
Vic ParkerUnderneath the Mango Tree: A Literary and Philosophical Exploration by Ahmet... Milton BellFollow ·2.2k
Milton BellFollow ·2.2k Douglas PowellFollow ·13.3k
Douglas PowellFollow ·13.3k Juan RulfoFollow ·4.6k
Juan RulfoFollow ·4.6k Henry JamesFollow ·5.1k
Henry JamesFollow ·5.1k Rod WardFollow ·4.7k
Rod WardFollow ·4.7k Ibrahim BlairFollow ·2k
Ibrahim BlairFollow ·2k Jermaine PowellFollow ·4.9k
Jermaine PowellFollow ·4.9k Gerald BellFollow ·17.4k
Gerald BellFollow ·17.4k

 Allen Parker
Allen ParkerChronic Wounds, Wound Dressings, and Wound Healing:...
Chronic wounds are a major challenge for...

 Ashton Reed
Ashton ReedThe Phantom Tree: A Novel New Timeslip that Transcends...
Prepare to be swept...

 Charles Bukowski
Charles BukowskiRobot World Cup XXI: Lecture Notes in Computer Science...
The 21st Robot World Cup...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6887 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 256 pages |